# loading packages
library(tidyverse)
library(lubridate)
library(janitor)3 Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
Learning Objectives of the Chapter
At the End of the Chapter, Students should be Able to -
Learn about the purpose of Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
Understand different techniques of transforming and cleaning data
Learn about Different R and Python Packages for EDA
Understand how to use six verbs for EDA
Perform EDA on some real world data sets
Learn about how to interpret results from EDA
3.1 Introduction
In descriptive statistics, we summarize the data using different metrics such as mean, median, standard deviation, minimum value, maximum value, and percentile. Descriptive statisics is also called summary statistics.
3.2 Data Collection & Importing
3.3 Data Cleaning
3.4 Packages for Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
In order to use pyjanitor, the data frame must be pandas because pyjanitor extends pandas data frame functionality.
# loading the package
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# from pyjanitor package
# pip install pyjanitor
import janitor
from janitor import clean_names, remove_empty3.5 Importing the Dataset
# importing data frame
df = read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/msharifbd/DATA/main/Al-Bundy_raw-data.csv")# importing data frame
df_pd = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/msharifbd/DATA/main/Al-Bundy_raw-data.csv")3.6 Meta Data
Meta data is data about the data. Before we put the data into analysis, we need to learn about our dataset. This learning invovles knowing about the number of rows, number of columns, the types of the fields, the appropriateness of those types, the missing values in the dataset and so on.
glimpse(df)Rows: 14,967
Columns: 14
$ InvoiceNo <dbl> 52389, 52390, 52391, 52392, 52393, 52394, 52395, 52396…
$ Date <chr> "1/1/2014", "1/1/2014", "1/1/2014", "1/1/2014", "1/1/2…
$ Country <chr> "United Kingdom", "United States", "Canada", "United S…
$ ProductID <dbl> 2152, 2230, 2160, 2234, 2222, 2173, 2200, 2238, 2191, …
$ Shop <chr> "UK2", "US15", "CAN7", "US6", "UK4", "US15", "GER2", "…
$ Gender <chr> "Male", "Male", "Male", "Female", "Female", "Male", "F…
$ `Size (US)` <dbl> 11.0, 11.5, 9.5, 9.5, 9.0, 10.5, 9.0, 10.0, 10.5, 9.0,…
$ `Size (Europe)` <chr> "44", "44-45", "42-43", "40", "39-40", "43-44", "39-40…
$ `Size (UK)` <dbl> 10.5, 11.0, 9.0, 7.5, 7.0, 10.0, 7.0, 9.5, 10.0, 7.0, …
$ UnitPrice <dbl> 159, 199, 149, 159, 159, 159, 179, 169, 139, 149, 129,…
$ Discount <dbl> 0.0, 0.2, 0.2, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0,…
$ Year <dbl> 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, …
$ Month <dbl> 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, …
$ SalePrice <dbl> 159.0, 159.2, 119.2, 159.0, 159.0, 159.0, 179.0, 169.0…map_df(df, ~sum(is.na(.))) |>
glimpse()Rows: 1
Columns: 14
$ InvoiceNo <int> 0
$ Date <int> 0
$ Country <int> 0
$ ProductID <int> 0
$ Shop <int> 0
$ Gender <int> 0
$ `Size (US)` <int> 0
$ `Size (Europe)` <int> 0
$ `Size (UK)` <int> 0
$ UnitPrice <int> 0
$ Discount <int> 0
$ Year <int> 0
$ Month <int> 0
$ SalePrice <int> 0ncol(df)[1] 14nrow(df)[1] 14967head(df)# A tibble: 6 × 14
InvoiceNo Date Country ProductID Shop Gender `Size (US)` `Size (Europe)`
<dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
1 52389 1/1/2014 United … 2152 UK2 Male 11 44
2 52390 1/1/2014 United … 2230 US15 Male 11.5 44-45
3 52391 1/1/2014 Canada 2160 CAN7 Male 9.5 42-43
4 52392 1/1/2014 United … 2234 US6 Female 9.5 40
5 52393 1/1/2014 United … 2222 UK4 Female 9 39-40
6 52394 1/1/2014 United … 2173 US15 Male 10.5 43-44
# ℹ 6 more variables: `Size (UK)` <dbl>, UnitPrice <dbl>, Discount <dbl>,
# Year <dbl>, Month <dbl>, SalePrice <dbl>tail(df)# A tibble: 6 × 14
InvoiceNo Date Country ProductID Shop Gender `Size (US)` `Size (Europe)`
<dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
1 65772 12/31/20… United… 2168 US13 Male 8 41
2 65773 12/31/20… United… 2154 UK2 Male 9.5 42-43
3 65774 12/31/20… United… 2181 US12 Female 12 42-43
4 65775 12/31/20… Canada 2203 CAN6 Male 10.5 43-44
5 65776 12/31/20… Germany 2231 GER1 Female 9.5 40
6 65777 12/31/20… Germany 2156 GER1 Female 6.5 37
# ℹ 6 more variables: `Size (UK)` <dbl>, UnitPrice <dbl>, Discount <dbl>,
# Year <dbl>, Month <dbl>, SalePrice <dbl>dplyr::sample_n(df, 10)# A tibble: 10 × 14
InvoiceNo Date Country ProductID Shop Gender `Size (US)` `Size (Europe)`
<dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
1 63306 8/15/20… Germany 2201 GER2 Male 10.5 43-44
2 57382 8/22/20… United… 2163 US12 Male 10 43
3 58279 10/27/2… Canada 2153 CAN6 Male 11 44
4 63508 8/25/20… United… 2173 US12 Male 9.5 42-43
5 61992 6/13/20… Canada 2193 CAN6 Male 10.5 43-44
6 54302 10/22/2… United… 2230 US12 Male 10.5 43-44
7 65410 12/5/20… Germany 2187 GER1 Male 8 41
8 64494 10/14/2… Germany 2198 GER2 Male 11.5 44-45
9 62202 6/23/20… United… 2191 US9 Female 7 37-38
10 58476 11/9/20… Germany 2147 GER2 Male 11.5 44-45
# ℹ 6 more variables: `Size (UK)` <dbl>, UnitPrice <dbl>, Discount <dbl>,
# Year <dbl>, Month <dbl>, SalePrice <dbl>df_pd.info()<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 14967 entries, 0 to 14966
Data columns (total 14 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 InvoiceNo 14967 non-null int64
1 Date 14967 non-null object
2 Country 14967 non-null object
3 ProductID 14967 non-null int64
4 Shop 14967 non-null object
5 Gender 14967 non-null object
6 Size (US) 14967 non-null float64
7 Size (Europe) 14967 non-null object
8 Size (UK) 14967 non-null float64
9 UnitPrice 14967 non-null int64
10 Discount 14967 non-null float64
11 Year 14967 non-null int64
12 Month 14967 non-null int64
13 SalePrice 14967 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(4), int64(5), object(5)
memory usage: 1.6+ MBdf_pd.shape(14967, 14)print('The total number of rows and columns of the product data is \
{} and {} respectively.'.format(df_pd.shape[0], df_pd.shape[1]))The total number of rows and columns of the product data is 14967 and 14 respectively.print(f'The total number of rows and columns of the product data is \
{df_pd.shape[0]} and {df_pd.shape[1]} respectively.')The total number of rows and columns of the product data is 14967 and 14 respectively.df_pd.columnsIndex(['InvoiceNo', 'Date', 'Country', 'ProductID', 'Shop', 'Gender',
'Size (US)', 'Size (Europe)', 'Size (UK)', 'UnitPrice', 'Discount',
'Year', 'Month', 'SalePrice'],
dtype='object')df_pd.head() InvoiceNo Date Country ... Year Month SalePrice
0 52389 1/1/2014 United Kingdom ... 2014 1 159.0
1 52390 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.2
2 52391 1/1/2014 Canada ... 2014 1 119.2
3 52392 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.0
4 52393 1/1/2014 United Kingdom ... 2014 1 159.0
[5 rows x 14 columns]df_pd.tail() InvoiceNo Date Country ... Year Month SalePrice
14962 65773 12/31/2016 United Kingdom ... 2016 12 139.0
14963 65774 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 149.0
14964 65775 12/31/2016 Canada ... 2016 12 125.3
14965 65776 12/31/2016 Germany ... 2016 12 199.0
14966 65777 12/31/2016 Germany ... 2016 12 125.1
[5 rows x 14 columns]df_pd.isna().sum()InvoiceNo 0
Date 0
Country 0
ProductID 0
Shop 0
Gender 0
Size (US) 0
Size (Europe) 0
Size (UK) 0
UnitPrice 0
Discount 0
Year 0
Month 0
SalePrice 0
dtype: int64df_pd.dtypesInvoiceNo int64
Date object
Country object
ProductID int64
Shop object
Gender object
Size (US) float64
Size (Europe) object
Size (UK) float64
UnitPrice int64
Discount float64
Year int64
Month int64
SalePrice float64
dtype: objectdf_pd.sample(n=10) InvoiceNo Date Country ... Year Month SalePrice
5390 57161 8/5/2015 United States ... 2015 8 149.0
8086 59630 1/29/2016 Canada ... 2016 1 159.0
5375 57146 8/3/2015 Canada ... 2015 8 159.0
7119 58756 11/29/2015 Germany ... 2015 11 89.5
927 53167 5/4/2014 United Kingdom ... 2014 5 118.3
2908 54876 1/17/2015 Germany ... 2015 1 125.1
11353 62542 7/9/2016 Germany ... 2016 7 179.0
10534 61811 6/4/2016 Canada ... 2016 6 139.0
6362 58052 10/11/2015 United States ... 2015 10 189.0
5119 56914 7/17/2015 Canada ... 2015 7 139.0
[10 rows x 14 columns]3.7 Cleaning the Dataset
df |>
rename_all(toupper) |>
janitor::clean_names() |>
rename_all(toupper) |>
glimpse()Rows: 14,967
Columns: 14
$ INVOICENO <dbl> 52389, 52390, 52391, 52392, 52393, 52394, 52395, 52396, 52…
$ DATE <chr> "1/1/2014", "1/1/2014", "1/1/2014", "1/1/2014", "1/1/2014"…
$ COUNTRY <chr> "United Kingdom", "United States", "Canada", "United State…
$ PRODUCTID <dbl> 2152, 2230, 2160, 2234, 2222, 2173, 2200, 2238, 2191, 2237…
$ SHOP <chr> "UK2", "US15", "CAN7", "US6", "UK4", "US15", "GER2", "CAN5…
$ GENDER <chr> "Male", "Male", "Male", "Female", "Female", "Male", "Femal…
$ SIZE_US <dbl> 11.0, 11.5, 9.5, 9.5, 9.0, 10.5, 9.0, 10.0, 10.5, 9.0, 10.…
$ SIZE_EUROPE <chr> "44", "44-45", "42-43", "40", "39-40", "43-44", "39-40", "…
$ SIZE_UK <dbl> 10.5, 11.0, 9.0, 7.5, 7.0, 10.0, 7.0, 9.5, 10.0, 7.0, 9.5,…
$ UNITPRICE <dbl> 159, 199, 149, 159, 159, 159, 179, 169, 139, 149, 129, 169…
$ DISCOUNT <dbl> 0.0, 0.2, 0.2, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.1…
$ YEAR <dbl> 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014…
$ MONTH <dbl> 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1…
$ SALEPRICE <dbl> 159.0, 159.2, 119.2, 159.0, 159.0, 159.0, 179.0, 169.0, 13…df = df |>
rename_all(toupper) |>
janitor::clean_names() |>
rename_all(toupper)
glimpse(df)Rows: 14,967
Columns: 14
$ INVOICENO <dbl> 52389, 52390, 52391, 52392, 52393, 52394, 52395, 52396, 52…
$ DATE <chr> "1/1/2014", "1/1/2014", "1/1/2014", "1/1/2014", "1/1/2014"…
$ COUNTRY <chr> "United Kingdom", "United States", "Canada", "United State…
$ PRODUCTID <dbl> 2152, 2230, 2160, 2234, 2222, 2173, 2200, 2238, 2191, 2237…
$ SHOP <chr> "UK2", "US15", "CAN7", "US6", "UK4", "US15", "GER2", "CAN5…
$ GENDER <chr> "Male", "Male", "Male", "Female", "Female", "Male", "Femal…
$ SIZE_US <dbl> 11.0, 11.5, 9.5, 9.5, 9.0, 10.5, 9.0, 10.0, 10.5, 9.0, 10.…
$ SIZE_EUROPE <chr> "44", "44-45", "42-43", "40", "39-40", "43-44", "39-40", "…
$ SIZE_UK <dbl> 10.5, 11.0, 9.0, 7.5, 7.0, 10.0, 7.0, 9.5, 10.0, 7.0, 9.5,…
$ UNITPRICE <dbl> 159, 199, 149, 159, 159, 159, 179, 169, 139, 149, 129, 169…
$ DISCOUNT <dbl> 0.0, 0.2, 0.2, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.1…
$ YEAR <dbl> 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014…
$ MONTH <dbl> 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1…
$ SALEPRICE <dbl> 159.0, 159.2, 119.2, 159.0, 159.0, 159.0, 179.0, 169.0, 13…df_pd.columns.str.upper().to_list()['INVOICENO', 'DATE', 'COUNTRY', 'PRODUCTID', 'SHOP', 'GENDER', 'SIZE (US)', 'SIZE (EUROPE)', 'SIZE (UK)', 'UNITPRICE', 'DISCOUNT', 'YEAR', 'MONTH', 'SALEPRICE'](df_pd
.pipe(remove_empty)
.pipe(lambda x: x.clean_names(case_type = "upper"))
.pipe(lambda x: x.rename(columns = {'SIZE_US_': 'SIZE_US', 'SIZE_EUROPE_':"SIZE_EUROPE", "SIZE_UK_":"SIZE_UK"}))
.pipe(lambda x: x.info())
)<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 14967 entries, 0 to 14966
Data columns (total 14 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 INVOICENO 14967 non-null int64
1 DATE 14967 non-null object
2 COUNTRY 14967 non-null object
3 PRODUCTID 14967 non-null int64
4 SHOP 14967 non-null object
5 GENDER 14967 non-null object
6 SIZE_US 14967 non-null float64
7 SIZE_EUROPE 14967 non-null object
8 SIZE_UK 14967 non-null float64
9 UNITPRICE 14967 non-null int64
10 DISCOUNT 14967 non-null float64
11 YEAR 14967 non-null int64
12 MONTH 14967 non-null int64
13 SALEPRICE 14967 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(4), int64(5), object(5)
memory usage: 1.6+ MB# Changing the names of the columns to uppercase
df_pd.rename(columns = str.upper, inplace = True)
df_pd.columnsIndex(['INVOICENO', 'DATE', 'COUNTRY', 'PRODUCTID', 'SHOP', 'GENDER',
'SIZE (US)', 'SIZE (EUROPE)', 'SIZE (UK)', 'UNITPRICE', 'DISCOUNT',
'YEAR', 'MONTH', 'SALEPRICE'],
dtype='object')new_column = df_pd.columns \
.str.replace("(", '').str.replace(")", "") \
.str.replace(' ','_') # Cleaning the names of the variables
new_columnIndex(['INVOICENO', 'DATE', 'COUNTRY', 'PRODUCTID', 'SHOP', 'GENDER',
'SIZE_US', 'SIZE_EUROPE', 'SIZE_UK', 'UNITPRICE', 'DISCOUNT', 'YEAR',
'MONTH', 'SALEPRICE'],
dtype='object')df_pd.columns = new_column
df_pd.columnsIndex(['INVOICENO', 'DATE', 'COUNTRY', 'PRODUCTID', 'SHOP', 'GENDER',
'SIZE_US', 'SIZE_EUROPE', 'SIZE_UK', 'UNITPRICE', 'DISCOUNT', 'YEAR',
'MONTH', 'SALEPRICE'],
dtype='object')df_pd.rename(columns=str.upper, inplace = True)
df_pd.columns Index(['INVOICENO', 'DATE', 'COUNTRY', 'PRODUCTID', 'SHOP', 'GENDER',
'SIZE_US', 'SIZE_EUROPE', 'SIZE_UK', 'UNITPRICE', 'DISCOUNT', 'YEAR',
'MONTH', 'SALEPRICE'],
dtype='object')3.7.1 Changing the Types of Variables
df |>
mutate (DATE = lubridate::mdy(DATE)) |>
glimpse()Rows: 14,967
Columns: 14
$ INVOICENO <dbl> 52389, 52390, 52391, 52392, 52393, 52394, 52395, 52396, 52…
$ DATE <date> 2014-01-01, 2014-01-01, 2014-01-01, 2014-01-01, 2014-01-0…
$ COUNTRY <chr> "United Kingdom", "United States", "Canada", "United State…
$ PRODUCTID <dbl> 2152, 2230, 2160, 2234, 2222, 2173, 2200, 2238, 2191, 2237…
$ SHOP <chr> "UK2", "US15", "CAN7", "US6", "UK4", "US15", "GER2", "CAN5…
$ GENDER <chr> "Male", "Male", "Male", "Female", "Female", "Male", "Femal…
$ SIZE_US <dbl> 11.0, 11.5, 9.5, 9.5, 9.0, 10.5, 9.0, 10.0, 10.5, 9.0, 10.…
$ SIZE_EUROPE <chr> "44", "44-45", "42-43", "40", "39-40", "43-44", "39-40", "…
$ SIZE_UK <dbl> 10.5, 11.0, 9.0, 7.5, 7.0, 10.0, 7.0, 9.5, 10.0, 7.0, 9.5,…
$ UNITPRICE <dbl> 159, 199, 149, 159, 159, 159, 179, 169, 139, 149, 129, 169…
$ DISCOUNT <dbl> 0.0, 0.2, 0.2, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.1…
$ YEAR <dbl> 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014…
$ MONTH <dbl> 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1…
$ SALEPRICE <dbl> 159.0, 159.2, 119.2, 159.0, 159.0, 159.0, 179.0, 169.0, 13… From the above, it is now evident the the type of the DATE variable now is date.
df |>
mutate (DATE = lubridate::mdy(DATE)) |>
mutate (PRODUCTID = as.character(PRODUCTID)) |>
glimpse()Rows: 14,967
Columns: 14
$ INVOICENO <dbl> 52389, 52390, 52391, 52392, 52393, 52394, 52395, 52396, 52…
$ DATE <date> 2014-01-01, 2014-01-01, 2014-01-01, 2014-01-01, 2014-01-0…
$ COUNTRY <chr> "United Kingdom", "United States", "Canada", "United State…
$ PRODUCTID <chr> "2152", "2230", "2160", "2234", "2222", "2173", "2200", "2…
$ SHOP <chr> "UK2", "US15", "CAN7", "US6", "UK4", "US15", "GER2", "CAN5…
$ GENDER <chr> "Male", "Male", "Male", "Female", "Female", "Male", "Femal…
$ SIZE_US <dbl> 11.0, 11.5, 9.5, 9.5, 9.0, 10.5, 9.0, 10.0, 10.5, 9.0, 10.…
$ SIZE_EUROPE <chr> "44", "44-45", "42-43", "40", "39-40", "43-44", "39-40", "…
$ SIZE_UK <dbl> 10.5, 11.0, 9.0, 7.5, 7.0, 10.0, 7.0, 9.5, 10.0, 7.0, 9.5,…
$ UNITPRICE <dbl> 159, 199, 149, 159, 159, 159, 179, 169, 139, 149, 129, 169…
$ DISCOUNT <dbl> 0.0, 0.2, 0.2, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.1…
$ YEAR <dbl> 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014…
$ MONTH <dbl> 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1…
$ SALEPRICE <dbl> 159.0, 159.2, 119.2, 159.0, 159.0, 159.0, 179.0, 169.0, 13… From the above, it is now evident the the type of the DATE and PRODUCTID variable now is date (date) and character (chr) respectively. We can now incorparte the changes into the data frame.
df = df |>
mutate (DATE = lubridate::mdy(DATE)) |>
mutate (PRODUCTID = as.character(PRODUCTID))
glimpse(df)Rows: 14,967
Columns: 14
$ INVOICENO <dbl> 52389, 52390, 52391, 52392, 52393, 52394, 52395, 52396, 52…
$ DATE <date> 2014-01-01, 2014-01-01, 2014-01-01, 2014-01-01, 2014-01-0…
$ COUNTRY <chr> "United Kingdom", "United States", "Canada", "United State…
$ PRODUCTID <chr> "2152", "2230", "2160", "2234", "2222", "2173", "2200", "2…
$ SHOP <chr> "UK2", "US15", "CAN7", "US6", "UK4", "US15", "GER2", "CAN5…
$ GENDER <chr> "Male", "Male", "Male", "Female", "Female", "Male", "Femal…
$ SIZE_US <dbl> 11.0, 11.5, 9.5, 9.5, 9.0, 10.5, 9.0, 10.0, 10.5, 9.0, 10.…
$ SIZE_EUROPE <chr> "44", "44-45", "42-43", "40", "39-40", "43-44", "39-40", "…
$ SIZE_UK <dbl> 10.5, 11.0, 9.0, 7.5, 7.0, 10.0, 7.0, 9.5, 10.0, 7.0, 9.5,…
$ UNITPRICE <dbl> 159, 199, 149, 159, 159, 159, 179, 169, 139, 149, 129, 169…
$ DISCOUNT <dbl> 0.0, 0.2, 0.2, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.1…
$ YEAR <dbl> 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014…
$ MONTH <dbl> 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1…
$ SALEPRICE <dbl> 159.0, 159.2, 119.2, 159.0, 159.0, 159.0, 179.0, 169.0, 13…(
df_pd
.pipe(lambda x: x.assign(DATE = pd.to_datetime(x['DATE'])))
.pipe(lambda x: x.info())
)<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 14967 entries, 0 to 14966
Data columns (total 14 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 INVOICENO 14967 non-null int64
1 DATE 14967 non-null datetime64[ns]
2 COUNTRY 14967 non-null object
3 PRODUCTID 14967 non-null int64
4 SHOP 14967 non-null object
5 GENDER 14967 non-null object
6 SIZE_US 14967 non-null float64
7 SIZE_EUROPE 14967 non-null object
8 SIZE_UK 14967 non-null float64
9 UNITPRICE 14967 non-null int64
10 DISCOUNT 14967 non-null float64
11 YEAR 14967 non-null int64
12 MONTH 14967 non-null int64
13 SALEPRICE 14967 non-null float64
dtypes: datetime64[ns](1), float64(4), int64(5), object(4)
memory usage: 1.6+ MB# converting integer to object
df_pd.INVOICENO = df_pd.INVOICENO.astype(str)
df_pd[['MONTH', 'PRODUCTID']] = df_pd[['MONTH', 'PRODUCTID']].astype(str)
df_pd.info()<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 14967 entries, 0 to 14966
Data columns (total 14 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 INVOICENO 14967 non-null object
1 DATE 14967 non-null object
2 COUNTRY 14967 non-null object
3 PRODUCTID 14967 non-null object
4 SHOP 14967 non-null object
5 GENDER 14967 non-null object
6 SIZE_US 14967 non-null float64
7 SIZE_EUROPE 14967 non-null object
8 SIZE_UK 14967 non-null float64
9 UNITPRICE 14967 non-null int64
10 DISCOUNT 14967 non-null float64
11 YEAR 14967 non-null int64
12 MONTH 14967 non-null object
13 SALEPRICE 14967 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(4), int64(2), object(8)
memory usage: 1.6+ MB3.8 Some Other Useful Functions
There are some other useful functions that can be used to explore the dataset for analysis. Some of those useful functions are discussed below.
df|> count(YEAR)# A tibble: 3 × 2
YEAR n
<dbl> <int>
1 2014 2753
2 2015 4848
3 2016 7366df|> count(COUNTRY)# A tibble: 4 × 2
COUNTRY n
<chr> <int>
1 Canada 2952
2 Germany 4392
3 United Kingdom 1737
4 United States 5886df|> distinct(COUNTRY)# A tibble: 4 × 1
COUNTRY
<chr>
1 United Kingdom
2 United States
3 Canada
4 Germany df_pd['YEAR'].value_counts()YEAR
2016 7366
2015 4848
2014 2753
Name: count, dtype: int64df_pd['YEAR'].unique()array([2014, 2015, 2016], dtype=int64)3.9 Six Verbs for EDA
Table 3.1 shows the comparable functions in both dplyr and pandas packages. These functions are very much important to perform exploratory data analysis in both R and Python. group_by (groupby in pandas) and summarize ()1 (agg () in pandas) are often used together; therefore, they are in the same group in Table 3.1.
3.9.1 1st Verb - filter () Function
Filter functions are used to subset a data frame based on rows, meaning that retaining rows that satisfy given conditions. Filtering rows is also called slicing2 becasue we obtain a set of elements by filtering.
df |> filter (YEAR == "2015")# A tibble: 4,848 × 14
INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY PRODUCTID SHOP GENDER SIZE_US SIZE_EUROPE
<dbl> <date> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
1 54725 2015-01-01 United States 2187 US7 Male 9.5 42-43
2 54726 2015-01-01 United States 2174 US3 Male 8.5 41-42
3 54727 2015-01-01 United States 2240 US11 Male 9 42
4 54728 2015-01-01 Germany 2220 GER2 Male 10 43
5 54729 2015-01-01 United Kingd… 2199 UK5 Male 9.5 42-43
6 54730 2015-01-01 Canada 2169 CAN7 Female 7 37-38
7 54731 2015-01-01 Germany 2188 GER1 Female 9.5 40
8 54732 2015-01-02 United Kingd… 2155 UK5 Female 10 40-41
9 54733 2015-01-02 United States 2173 US5 Female 9 39-40
10 54734 2015-01-02 Germany 2222 GER3 Female 7.5 38
# ℹ 4,838 more rows
# ℹ 6 more variables: SIZE_UK <dbl>, UNITPRICE <dbl>, DISCOUNT <dbl>,
# YEAR <dbl>, MONTH <dbl>, SALEPRICE <dbl>df |> filter (COUNTRY %in% c("United States", "Canada"))# A tibble: 8,838 × 14
INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY PRODUCTID SHOP GENDER SIZE_US SIZE_EUROPE
<dbl> <date> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
1 52390 2014-01-01 United States 2230 US15 Male 11.5 44-45
2 52391 2014-01-01 Canada 2160 CAN7 Male 9.5 42-43
3 52392 2014-01-01 United States 2234 US6 Female 9.5 40
4 52394 2014-01-01 United States 2173 US15 Male 10.5 43-44
5 52396 2014-01-02 Canada 2238 CAN5 Male 10 43
6 52397 2014-01-02 United States 2191 US13 Male 10.5 43-44
7 52399 2014-01-02 United States 2197 US1 Male 10 43
8 52399 2014-01-02 United States 2213 US11 Female 9.5 40
9 52399 2014-01-02 United States 2206 US2 Female 9.5 40
10 52400 2014-01-02 United States 2152 US15 Male 8 41
# ℹ 8,828 more rows
# ℹ 6 more variables: SIZE_UK <dbl>, UNITPRICE <dbl>, DISCOUNT <dbl>,
# YEAR <dbl>, MONTH <dbl>, SALEPRICE <dbl>df |> filter (COUNTRY == "United States", YEAR == "2016")# A tibble: 2,935 × 14
INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY PRODUCTID SHOP GENDER SIZE_US SIZE_EUROPE
<dbl> <date> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
1 59206 2016-01-02 United States 2186 US13 Female 8 38-39
2 59209 2016-01-02 United States 2193 US14 Female 9 39-40
3 59213 2016-01-02 United States 2228 US13 Male 9.5 42-43
4 59214 2016-01-02 United States 2177 US12 Female 10.5 41
5 59214 2016-01-02 United States 2236 US6 Male 8.5 41-42
6 59219 2016-01-03 United States 2188 US14 Female 9.5 40
7 59221 2016-01-03 United States 2178 US13 Female 8 38-39
8 59223 2016-01-03 United States 2158 US3 Male 8 41
9 59225 2016-01-03 United States 2236 US13 Male 8 41
10 59226 2016-01-03 United States 2207 US14 Male 14 47
# ℹ 2,925 more rows
# ℹ 6 more variables: SIZE_UK <dbl>, UNITPRICE <dbl>, DISCOUNT <dbl>,
# YEAR <dbl>, MONTH <dbl>, SALEPRICE <dbl>df |> filter (COUNTRY == "United States", YEAR %in% c("2015","2016"))# A tibble: 4,859 × 14
INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY PRODUCTID SHOP GENDER SIZE_US SIZE_EUROPE
<dbl> <date> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
1 54725 2015-01-01 United States 2187 US7 Male 9.5 42-43
2 54726 2015-01-01 United States 2174 US3 Male 8.5 41-42
3 54727 2015-01-01 United States 2240 US11 Male 9 42
4 54733 2015-01-02 United States 2173 US5 Female 9 39-40
5 54738 2015-01-02 United States 2226 US3 Male 10 43
6 54739 2015-01-02 United States 2199 US11 Male 9.5 42-43
7 54742 2015-01-03 United States 2209 US6 Male 10 43
8 54743 2015-01-03 United States 2238 US15 Female 7.5 38
9 54745 2015-01-04 United States 2214 US12 Male 10.5 43-44
10 54749 2015-01-04 United States 2162 US15 Male 9.5 42-43
# ℹ 4,849 more rows
# ℹ 6 more variables: SIZE_UK <dbl>, UNITPRICE <dbl>, DISCOUNT <dbl>,
# YEAR <dbl>, MONTH <dbl>, SALEPRICE <dbl>df |> filter (COUNTRY %in% c("United States", "Canada"), YEAR == "2014")# A tibble: 1,649 × 14
INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY PRODUCTID SHOP GENDER SIZE_US SIZE_EUROPE
<dbl> <date> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
1 52390 2014-01-01 United States 2230 US15 Male 11.5 44-45
2 52391 2014-01-01 Canada 2160 CAN7 Male 9.5 42-43
3 52392 2014-01-01 United States 2234 US6 Female 9.5 40
4 52394 2014-01-01 United States 2173 US15 Male 10.5 43-44
5 52396 2014-01-02 Canada 2238 CAN5 Male 10 43
6 52397 2014-01-02 United States 2191 US13 Male 10.5 43-44
7 52399 2014-01-02 United States 2197 US1 Male 10 43
8 52399 2014-01-02 United States 2213 US11 Female 9.5 40
9 52399 2014-01-02 United States 2206 US2 Female 9.5 40
10 52400 2014-01-02 United States 2152 US15 Male 8 41
# ℹ 1,639 more rows
# ℹ 6 more variables: SIZE_UK <dbl>, UNITPRICE <dbl>, DISCOUNT <dbl>,
# YEAR <dbl>, MONTH <dbl>, SALEPRICE <dbl>df_pd.query("YEAR == 2015") INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY ... YEAR MONTH SALEPRICE
2753 54725 1/1/2015 United States ... 2015 1 179.0
2754 54726 1/1/2015 United States ... 2015 1 169.0
2755 54727 1/1/2015 United States ... 2015 1 116.1
2756 54728 1/1/2015 Germany ... 2015 1 129.0
2757 54729 1/1/2015 United Kingdom ... 2015 1 139.0
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
7596 59192 12/31/2015 United States ... 2015 12 79.5
7597 59193 12/31/2015 United States ... 2015 12 139.0
7598 59194 12/31/2015 Germany ... 2015 12 159.0
7599 59195 12/31/2015 Germany ... 2015 12 149.0
7600 59196 12/31/2015 United States ... 2015 12 179.0
[4848 rows x 14 columns]df_pd.query('COUNTRY== "United States" | COUNTRY == "Canada"') INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY ... YEAR MONTH SALEPRICE
1 52390 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.2
2 52391 1/1/2014 Canada ... 2014 1 119.2
3 52392 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.0
5 52394 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.0
7 52396 1/2/2014 Canada ... 2014 1 169.0
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
14959 65770 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 119.2
14960 65771 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 189.0
14961 65772 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 129.0
14963 65774 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 149.0
14964 65775 12/31/2016 Canada ... 2016 12 125.3
[8838 rows x 14 columns]df_pd.query("COUNTRY in ['United States', 'Canada']") INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY ... YEAR MONTH SALEPRICE
1 52390 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.2
2 52391 1/1/2014 Canada ... 2014 1 119.2
3 52392 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.0
5 52394 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.0
7 52396 1/2/2014 Canada ... 2014 1 169.0
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
14959 65770 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 119.2
14960 65771 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 189.0
14961 65772 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 129.0
14963 65774 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 149.0
14964 65775 12/31/2016 Canada ... 2016 12 125.3
[8838 rows x 14 columns]df_pd.query("COUNTRY== 'United States' & YEAR== 2016") INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY ... YEAR MONTH SALEPRICE
7610 59206 1/2/2016 United States ... 2016 1 132.3
7613 59209 1/2/2016 United States ... 2016 1 127.2
7617 59213 1/2/2016 United States ... 2016 1 125.3
7618 59214 1/2/2016 United States ... 2016 1 151.2
7619 59214 1/2/2016 United States ... 2016 1 151.2
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
14956 65767 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 139.0
14959 65770 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 119.2
14960 65771 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 189.0
14961 65772 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 129.0
14963 65774 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 149.0
[2935 rows x 14 columns]df_pd.query("COUNTRY== 'United States' & YEAR in [2015,2016]") INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY ... YEAR MONTH SALEPRICE
2753 54725 1/1/2015 United States ... 2015 1 179.0
2754 54726 1/1/2015 United States ... 2015 1 169.0
2755 54727 1/1/2015 United States ... 2015 1 116.1
2761 54733 1/2/2015 United States ... 2015 1 179.0
2766 54738 1/2/2015 United States ... 2015 1 199.0
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
14956 65767 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 139.0
14959 65770 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 119.2
14960 65771 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 189.0
14961 65772 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 129.0
14963 65774 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 149.0
[4859 rows x 14 columns]df_pd[df_pd['COUNTRY'] == "United States"] INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY ... YEAR MONTH SALEPRICE
1 52390 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.2
3 52392 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.0
5 52394 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.0
8 52397 1/2/2014 United States ... 2014 1 139.0
10 52399 1/2/2014 United States ... 2014 1 129.0
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
14956 65767 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 139.0
14959 65770 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 119.2
14960 65771 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 189.0
14961 65772 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 129.0
14963 65774 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 149.0
[5886 rows x 14 columns]df_pd.loc[(df_pd['COUNTRY']=="United States")] INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY ... YEAR MONTH SALEPRICE
1 52390 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.2
3 52392 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.0
5 52394 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.0
8 52397 1/2/2014 United States ... 2014 1 139.0
10 52399 1/2/2014 United States ... 2014 1 129.0
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
14956 65767 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 139.0
14959 65770 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 119.2
14960 65771 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 189.0
14961 65772 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 129.0
14963 65774 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 149.0
[5886 rows x 14 columns]df_pd.loc[df_pd['COUNTRY'].isin(["United States", "Canada"])] INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY ... YEAR MONTH SALEPRICE
1 52390 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.2
2 52391 1/1/2014 Canada ... 2014 1 119.2
3 52392 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.0
5 52394 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.0
7 52396 1/2/2014 Canada ... 2014 1 169.0
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
14959 65770 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 119.2
14960 65771 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 189.0
14961 65772 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 129.0
14963 65774 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 149.0
14964 65775 12/31/2016 Canada ... 2016 12 125.3
[8838 rows x 14 columns]df_pd.loc[df_pd['COUNTRY']\
.isin(["United States", "Canada"]) &(df_pd['YEAR']==2014)] INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY ... YEAR MONTH SALEPRICE
1 52390 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.2
2 52391 1/1/2014 Canada ... 2014 1 119.2
3 52392 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.0
5 52394 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.0
7 52396 1/2/2014 Canada ... 2014 1 169.0
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
2739 54713 12/30/2014 United States ... 2014 12 189.0
2745 54718 12/31/2014 Canada ... 2014 12 151.2
2746 54719 12/31/2014 United States ... 2014 12 199.0
2748 54721 12/31/2014 Canada ... 2014 12 74.5
2749 54722 12/31/2014 United States ... 2014 12 118.3
[1649 rows x 14 columns]df_pd.loc[(df_pd['COUNTRY']=="United States") &(df_pd ["YEAR"] ==2014)] INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY ... YEAR MONTH SALEPRICE
1 52390 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.2
3 52392 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.0
5 52394 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.0
8 52397 1/2/2014 United States ... 2014 1 139.0
10 52399 1/2/2014 United States ... 2014 1 129.0
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
2731 54705 12/29/2014 United States ... 2014 12 179.0
2734 54708 12/30/2014 United States ... 2014 12 159.0
2739 54713 12/30/2014 United States ... 2014 12 189.0
2746 54719 12/31/2014 United States ... 2014 12 199.0
2749 54722 12/31/2014 United States ... 2014 12 118.3
[1027 rows x 14 columns]df_pd.loc[df_pd['COUNTRY'] == "United States", :] INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY ... YEAR MONTH SALEPRICE
1 52390 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.2
3 52392 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.0
5 52394 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.0
8 52397 1/2/2014 United States ... 2014 1 139.0
10 52399 1/2/2014 United States ... 2014 1 129.0
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
14956 65767 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 139.0
14959 65770 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 119.2
14960 65771 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 189.0
14961 65772 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 129.0
14963 65774 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 149.0
[5886 rows x 14 columns]df_pd.loc[
df_pd['COUNTRY']=='United States',
['COUNTRY', "UNITPRICE", "SALEPRICE"]] COUNTRY UNITPRICE SALEPRICE
1 United States 199 159.2
3 United States 159 159.0
5 United States 159 159.0
8 United States 139 139.0
10 United States 129 129.0
... ... ... ...
14956 United States 139 139.0
14959 United States 149 119.2
14960 United States 189 189.0
14961 United States 129 129.0
14963 United States 149 149.0
[5886 rows x 3 columns]3.9.2 2nd Verb - arrange () Function
In arrange functions, we order the rows of a data frame by the values of given columns. It is like sorting or odering the data.
df |>
arrange(DATE) # A tibble: 14,967 × 14
INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY PRODUCTID SHOP GENDER SIZE_US SIZE_EUROPE
<dbl> <date> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
1 52389 2014-01-01 United Kingd… 2152 UK2 Male 11 44
2 52390 2014-01-01 United States 2230 US15 Male 11.5 44-45
3 52391 2014-01-01 Canada 2160 CAN7 Male 9.5 42-43
4 52392 2014-01-01 United States 2234 US6 Female 9.5 40
5 52393 2014-01-01 United Kingd… 2222 UK4 Female 9 39-40
6 52394 2014-01-01 United States 2173 US15 Male 10.5 43-44
7 52395 2014-01-02 Germany 2200 GER2 Female 9 39-40
8 52396 2014-01-02 Canada 2238 CAN5 Male 10 43
9 52397 2014-01-02 United States 2191 US13 Male 10.5 43-44
10 52398 2014-01-02 United Kingd… 2237 UK1 Female 9 39-40
# ℹ 14,957 more rows
# ℹ 6 more variables: SIZE_UK <dbl>, UNITPRICE <dbl>, DISCOUNT <dbl>,
# YEAR <dbl>, MONTH <dbl>, SALEPRICE <dbl>df |>
arrange(desc(DATE)) # A tibble: 14,967 × 14
INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY PRODUCTID SHOP GENDER SIZE_US SIZE_EUROPE
<dbl> <date> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
1 65765 2016-12-31 Canada 2199 CAN5 Male 11 44
2 65766 2016-12-31 United Kingd… 2202 UK1 Male 9.5 42-43
3 65767 2016-12-31 United States 2147 US15 Male 9.5 42-43
4 65768 2016-12-31 Germany 2205 GER1 Female 7.5 38
5 65769 2016-12-31 Germany 2210 GER2 Male 10.5 43-44
6 65770 2016-12-31 United States 2178 US13 Female 8 38-39
7 65771 2016-12-31 United States 2209 US15 Male 9 42
8 65772 2016-12-31 United States 2168 US13 Male 8 41
9 65773 2016-12-31 United Kingd… 2154 UK2 Male 9.5 42-43
10 65774 2016-12-31 United States 2181 US12 Female 12 42-43
# ℹ 14,957 more rows
# ℹ 6 more variables: SIZE_UK <dbl>, UNITPRICE <dbl>, DISCOUNT <dbl>,
# YEAR <dbl>, MONTH <dbl>, SALEPRICE <dbl>df |>
arrange(MONTH, SALEPRICE) # A tibble: 14,967 × 14
INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY PRODUCTID SHOP GENDER SIZE_US SIZE_EUROPE
<dbl> <date> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
1 52414 2014-01-05 Germany 2239 GER2 Female 8.5 39
2 52533 2014-01-25 Canada 2151 CAN5 Female 9 39-40
3 52539 2014-01-26 United Kingd… 2227 UK1 Female 7.5 38
4 52548 2014-01-27 United Kingd… 2224 UK3 Male 8.5 41-42
5 54734 2015-01-02 Germany 2222 GER3 Female 7.5 38
6 54772 2015-01-06 Germany 2159 GER1 Male 12 45
7 54864 2015-01-16 Germany 2239 GER2 Female 7.5 38
8 54989 2015-01-28 Canada 2152 CAN6 Female 8 38-39
9 59220 2016-01-03 Canada 2202 CAN7 Male 10.5 43-44
10 59242 2016-01-04 United States 2231 US9 Female 9 39-40
# ℹ 14,957 more rows
# ℹ 6 more variables: SIZE_UK <dbl>, UNITPRICE <dbl>, DISCOUNT <dbl>,
# YEAR <dbl>, MONTH <dbl>, SALEPRICE <dbl>df_pd.sort_values(by =['DATE']) INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY ... YEAR MONTH SALEPRICE
0 52389 1/1/2014 United Kingdom ... 2014 1 159.0
1 52390 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.2
2 52391 1/1/2014 Canada ... 2014 1 119.2
3 52392 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.0
4 52393 1/1/2014 United Kingdom ... 2014 1 159.0
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
12785 63807 9/9/2016 Germany ... 2016 9 189.0
12786 63808 9/9/2016 Germany ... 2016 9 129.0
12787 63809 9/9/2016 United States ... 2016 9 179.0
12789 63811 9/9/2016 United States ... 2016 9 125.3
12779 63802 9/9/2016 United States ... 2016 9 125.1
[14967 rows x 14 columns]df_pd.sort_values(by =['DATE'], ascending = False) INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY ... YEAR MONTH SALEPRICE
12778 63802 9/9/2016 United States ... 2016 9 139.0
12784 63806 9/9/2016 Germany ... 2016 9 139.0
12773 63797 9/9/2016 Germany ... 2016 9 90.3
12772 63796 9/9/2016 Germany ... 2016 9 111.3
12771 63795 9/9/2016 Germany ... 2016 9 152.1
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
5 52394 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.0
4 52393 1/1/2014 United Kingdom ... 2014 1 159.0
3 52392 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.0
2 52391 1/1/2014 Canada ... 2014 1 119.2
0 52389 1/1/2014 United Kingdom ... 2014 1 159.0
[14967 rows x 14 columns]df_pd.sort_values(by =['MONTH', 'SALEPRICE']) INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY ... YEAR MONTH SALEPRICE
33 52414 1/5/2014 Germany ... 2014 1 64.5
177 52533 1/25/2014 Canada ... 2014 1 64.5
185 52539 1/26/2014 United Kingdom ... 2014 1 64.5
194 52548 1/27/2014 United Kingdom ... 2014 1 64.5
2762 54734 1/2/2015 Germany ... 2015 1 64.5
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
13245 64219 9/29/2016 United Kingdom ... 2016 9 199.0
13246 64220 9/29/2016 United States ... 2016 9 199.0
13248 64222 9/29/2016 United States ... 2016 9 199.0
13251 64224 9/29/2016 Germany ... 2016 9 199.0
13272 64244 9/30/2016 United States ... 2016 9 199.0
[14967 rows x 14 columns]3.9.3 3rd Verb - select () Function
Select functions help to select or obtain columns from the data frame. When there are a lot of columns in our dataset, select functions become very useful.
df |> select(DATE, UNITPRICE, DISCOUNT) # A tibble: 14,967 × 3
DATE UNITPRICE DISCOUNT
<date> <dbl> <dbl>
1 2014-01-01 159 0
2 2014-01-01 199 0.2
3 2014-01-01 149 0.2
4 2014-01-01 159 0
5 2014-01-01 159 0
6 2014-01-01 159 0
7 2014-01-02 179 0
8 2014-01-02 169 0
9 2014-01-02 139 0
10 2014-01-02 149 0
# ℹ 14,957 more rowsdf |> select(1:2, 5:8) # A tibble: 14,967 × 6
INVOICENO DATE SHOP GENDER SIZE_US SIZE_EUROPE
<dbl> <date> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
1 52389 2014-01-01 UK2 Male 11 44
2 52390 2014-01-01 US15 Male 11.5 44-45
3 52391 2014-01-01 CAN7 Male 9.5 42-43
4 52392 2014-01-01 US6 Female 9.5 40
5 52393 2014-01-01 UK4 Female 9 39-40
6 52394 2014-01-01 US15 Male 10.5 43-44
7 52395 2014-01-02 GER2 Female 9 39-40
8 52396 2014-01-02 CAN5 Male 10 43
9 52397 2014-01-02 US13 Male 10.5 43-44
10 52398 2014-01-02 UK1 Female 9 39-40
# ℹ 14,957 more rowsdf |>
select(starts_with('SIZE'))# A tibble: 14,967 × 3
SIZE_US SIZE_EUROPE SIZE_UK
<dbl> <chr> <dbl>
1 11 44 10.5
2 11.5 44-45 11
3 9.5 42-43 9
4 9.5 40 7.5
5 9 39-40 7
6 10.5 43-44 10
7 9 39-40 7
8 10 43 9.5
9 10.5 43-44 10
10 9 39-40 7
# ℹ 14,957 more rowsdf |>
select(ends_with('PRICE'))# A tibble: 14,967 × 2
UNITPRICE SALEPRICE
<dbl> <dbl>
1 159 159
2 199 159.
3 149 119.
4 159 159
5 159 159
6 159 159
7 179 179
8 169 169
9 139 139
10 149 149
# ℹ 14,957 more rowsdf |>
select(contains("_"))# A tibble: 14,967 × 3
SIZE_US SIZE_EUROPE SIZE_UK
<dbl> <chr> <dbl>
1 11 44 10.5
2 11.5 44-45 11
3 9.5 42-43 9
4 9.5 40 7.5
5 9 39-40 7
6 10.5 43-44 10
7 9 39-40 7
8 10 43 9.5
9 10.5 43-44 10
10 9 39-40 7
# ℹ 14,957 more rowsdf |>
select(matches("SIZE"))# A tibble: 14,967 × 3
SIZE_US SIZE_EUROPE SIZE_UK
<dbl> <chr> <dbl>
1 11 44 10.5
2 11.5 44-45 11
3 9.5 42-43 9
4 9.5 40 7.5
5 9 39-40 7
6 10.5 43-44 10
7 9 39-40 7
8 10 43 9.5
9 10.5 43-44 10
10 9 39-40 7
# ℹ 14,957 more rowsdf |>
select(matches("PRICE$"))# A tibble: 14,967 × 2
UNITPRICE SALEPRICE
<dbl> <dbl>
1 159 159
2 199 159.
3 149 119.
4 159 159
5 159 159
6 159 159
7 179 179
8 169 169
9 139 139
10 149 149
# ℹ 14,957 more rows# starts with letter S
df |>
select(matches("^S"))# A tibble: 14,967 × 5
SHOP SIZE_US SIZE_EUROPE SIZE_UK SALEPRICE
<chr> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 UK2 11 44 10.5 159
2 US15 11.5 44-45 11 159.
3 CAN7 9.5 42-43 9 119.
4 US6 9.5 40 7.5 159
5 UK4 9 39-40 7 159
6 US15 10.5 43-44 10 159
7 GER2 9 39-40 7 179
8 CAN5 10 43 9.5 169
9 US13 10.5 43-44 10 139
10 UK1 9 39-40 7 149
# ℹ 14,957 more rowsdf |>
select(where(is.character))# A tibble: 14,967 × 5
COUNTRY PRODUCTID SHOP GENDER SIZE_EUROPE
<chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
1 United Kingdom 2152 UK2 Male 44
2 United States 2230 US15 Male 44-45
3 Canada 2160 CAN7 Male 42-43
4 United States 2234 US6 Female 40
5 United Kingdom 2222 UK4 Female 39-40
6 United States 2173 US15 Male 43-44
7 Germany 2200 GER2 Female 39-40
8 Canada 2238 CAN5 Male 43
9 United States 2191 US13 Male 43-44
10 United Kingdom 2237 UK1 Female 39-40
# ℹ 14,957 more rowsdf |>
select(where(is.numeric))# A tibble: 14,967 × 8
INVOICENO SIZE_US SIZE_UK UNITPRICE DISCOUNT YEAR MONTH SALEPRICE
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 52389 11 10.5 159 0 2014 1 159
2 52390 11.5 11 199 0.2 2014 1 159.
3 52391 9.5 9 149 0.2 2014 1 119.
4 52392 9.5 7.5 159 0 2014 1 159
5 52393 9 7 159 0 2014 1 159
6 52394 10.5 10 159 0 2014 1 159
7 52395 9 7 179 0 2014 1 179
8 52396 10 9.5 169 0 2014 1 169
9 52397 10.5 10 139 0 2014 1 139
10 52398 9 7 149 0 2014 1 149
# ℹ 14,957 more rowsdf |>
select(MONTH, YEAR, everything())# A tibble: 14,967 × 14
MONTH YEAR INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY PRODUCTID SHOP GENDER SIZE_US
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <date> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
1 1 2014 52389 2014-01-01 United Kingd… 2152 UK2 Male 11
2 1 2014 52390 2014-01-01 United States 2230 US15 Male 11.5
3 1 2014 52391 2014-01-01 Canada 2160 CAN7 Male 9.5
4 1 2014 52392 2014-01-01 United States 2234 US6 Female 9.5
5 1 2014 52393 2014-01-01 United Kingd… 2222 UK4 Female 9
6 1 2014 52394 2014-01-01 United States 2173 US15 Male 10.5
7 1 2014 52395 2014-01-02 Germany 2200 GER2 Female 9
8 1 2014 52396 2014-01-02 Canada 2238 CAN5 Male 10
9 1 2014 52397 2014-01-02 United States 2191 US13 Male 10.5
10 1 2014 52398 2014-01-02 United Kingd… 2237 UK1 Female 9
# ℹ 14,957 more rows
# ℹ 5 more variables: SIZE_EUROPE <chr>, SIZE_UK <dbl>, UNITPRICE <dbl>,
# DISCOUNT <dbl>, SALEPRICE <dbl># any_of () vs all_of ()
df |>
select(any_of(c("PRICE", "SIZE")))# A tibble: 14,967 × 0# Dropping columns
df |>
select(-DATE)# A tibble: 14,967 × 13
INVOICENO COUNTRY PRODUCTID SHOP GENDER SIZE_US SIZE_EUROPE SIZE_UK
<dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <dbl>
1 52389 United Kingdom 2152 UK2 Male 11 44 10.5
2 52390 United States 2230 US15 Male 11.5 44-45 11
3 52391 Canada 2160 CAN7 Male 9.5 42-43 9
4 52392 United States 2234 US6 Female 9.5 40 7.5
5 52393 United Kingdom 2222 UK4 Female 9 39-40 7
6 52394 United States 2173 US15 Male 10.5 43-44 10
7 52395 Germany 2200 GER2 Female 9 39-40 7
8 52396 Canada 2238 CAN5 Male 10 43 9.5
9 52397 United States 2191 US13 Male 10.5 43-44 10
10 52398 United Kingdom 2237 UK1 Female 9 39-40 7
# ℹ 14,957 more rows
# ℹ 5 more variables: UNITPRICE <dbl>, DISCOUNT <dbl>, YEAR <dbl>, MONTH <dbl>,
# SALEPRICE <dbl>df_pd['DATE'] 0 1/1/2014
1 1/1/2014
2 1/1/2014
3 1/1/2014
4 1/1/2014
...
14962 12/31/2016
14963 12/31/2016
14964 12/31/2016
14965 12/31/2016
14966 12/31/2016
Name: DATE, Length: 14967, dtype: objectdf_pd[['DATE', 'UNITPRICE']] DATE UNITPRICE
0 1/1/2014 159
1 1/1/2014 199
2 1/1/2014 149
3 1/1/2014 159
4 1/1/2014 159
... ... ...
14962 12/31/2016 139
14963 12/31/2016 149
14964 12/31/2016 179
14965 12/31/2016 199
14966 12/31/2016 139
[14967 rows x 2 columns]df_pd.loc[:,['DATE', 'UNITPRICE']] DATE UNITPRICE
0 1/1/2014 159
1 1/1/2014 199
2 1/1/2014 149
3 1/1/2014 159
4 1/1/2014 159
... ... ...
14962 12/31/2016 139
14963 12/31/2016 149
14964 12/31/2016 179
14965 12/31/2016 199
14966 12/31/2016 139
[14967 rows x 2 columns]df_pd.iloc[:,5:8] GENDER SIZE_US SIZE_EUROPE
0 Male 11.0 44
1 Male 11.5 44-45
2 Male 9.5 42-43
3 Female 9.5 40
4 Female 9.0 39-40
... ... ... ...
14962 Male 9.5 42-43
14963 Female 12.0 42-43
14964 Male 10.5 43-44
14965 Female 9.5 40
14966 Female 6.5 37
[14967 rows x 3 columns]df_pd.iloc[:,[3,5,8]] PRODUCTID GENDER SIZE_UK
0 2152 Male 10.5
1 2230 Male 11.0
2 2160 Male 9.0
3 2234 Female 7.5
4 2222 Female 7.0
... ... ... ...
14962 2154 Male 9.0
14963 2181 Female 10.0
14964 2203 Male 10.0
14965 2231 Female 7.5
14966 2156 Female 4.5
[14967 rows x 3 columns]df_pd.filter(['YEAR','SALEPRICE', 'DISCOUNT', 'UNITPRICE']) YEAR SALEPRICE DISCOUNT UNITPRICE
0 2014 159.0 0.0 159
1 2014 159.2 0.2 199
2 2014 119.2 0.2 149
3 2014 159.0 0.0 159
4 2014 159.0 0.0 159
... ... ... ... ...
14962 2016 139.0 0.0 139
14963 2016 149.0 0.0 149
14964 2016 125.3 0.3 179
14965 2016 199.0 0.0 199
14966 2016 125.1 0.1 139
[14967 rows x 4 columns]df_pd.filter(['YEAR','SALEPRICE', 'DISCOUNT', 'UNITPRICE']) YEAR SALEPRICE DISCOUNT UNITPRICE
0 2014 159.0 0.0 159
1 2014 159.2 0.2 199
2 2014 119.2 0.2 149
3 2014 159.0 0.0 159
4 2014 159.0 0.0 159
... ... ... ... ...
14962 2016 139.0 0.0 139
14963 2016 149.0 0.0 149
14964 2016 125.3 0.3 179
14965 2016 199.0 0.0 199
14966 2016 125.1 0.1 139
[14967 rows x 4 columns] #RegularExpression(Regex)
df_pd.filter(regex ="PRICE$") #Ends with Price UNITPRICE SALEPRICE
0 159 159.0
1 199 159.2
2 149 119.2
3 159 159.0
4 159 159.0
... ... ...
14962 139 139.0
14963 149 149.0
14964 179 125.3
14965 199 199.0
14966 139 125.1
[14967 rows x 2 columns]df_pd.filter(regex ="ˆSIZE") #Starts with SIZEEmpty DataFrame
Columns: []
Index: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99, ...]
[14967 rows x 0 columns]df_pd.filter(regex ="PRICE") #Contains the word Price UNITPRICE SALEPRICE
0 159 159.0
1 199 159.2
2 149 119.2
3 159 159.0
4 159 159.0
... ... ...
14962 139 139.0
14963 149 149.0
14964 179 125.3
14965 199 199.0
14966 139 125.1
[14967 rows x 2 columns]df_pd.select_dtypes('object') INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY ... GENDER SIZE_EUROPE MONTH
0 52389 1/1/2014 United Kingdom ... Male 44 1
1 52390 1/1/2014 United States ... Male 44-45 1
2 52391 1/1/2014 Canada ... Male 42-43 1
3 52392 1/1/2014 United States ... Female 40 1
4 52393 1/1/2014 United Kingdom ... Female 39-40 1
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
14962 65773 12/31/2016 United Kingdom ... Male 42-43 12
14963 65774 12/31/2016 United States ... Female 42-43 12
14964 65775 12/31/2016 Canada ... Male 43-44 12
14965 65776 12/31/2016 Germany ... Female 40 12
14966 65777 12/31/2016 Germany ... Female 37 12
[14967 rows x 8 columns]df_pd.select_dtypes('int') UNITPRICE YEAR
0 159 2014
1 199 2014
2 149 2014
3 159 2014
4 159 2014
... ... ...
14962 139 2016
14963 149 2016
14964 179 2016
14965 199 2016
14966 139 2016
[14967 rows x 2 columns]df_pd.loc[:,df_pd.columns.str.startswith('SIZE')] SIZE_US SIZE_EUROPE SIZE_UK
0 11.0 44 10.5
1 11.5 44-45 11.0
2 9.5 42-43 9.0
3 9.5 40 7.5
4 9.0 39-40 7.0
... ... ... ...
14962 9.5 42-43 9.0
14963 12.0 42-43 10.0
14964 10.5 43-44 10.0
14965 9.5 40 7.5
14966 6.5 37 4.5
[14967 rows x 3 columns]df_pd.loc[:,df_pd.columns.str.contains('PRICE')] UNITPRICE SALEPRICE
0 159 159.0
1 199 159.2
2 149 119.2
3 159 159.0
4 159 159.0
... ... ...
14962 139 139.0
14963 149 149.0
14964 179 125.3
14965 199 199.0
14966 139 125.1
[14967 rows x 2 columns]df_pd.loc[:,df_pd.columns.str.endswith('PRICE')] UNITPRICE SALEPRICE
0 159 159.0
1 199 159.2
2 149 119.2
3 159 159.0
4 159 159.0
... ... ...
14962 139 139.0
14963 149 149.0
14964 179 125.3
14965 199 199.0
14966 139 125.1
[14967 rows x 2 columns]# Dropping columns
df_pd.drop(columns =['SIZE_EUROPE', 'SIZE_UK'], axis=1) INVOICENO DATE COUNTRY ... YEAR MONTH SALEPRICE
0 52389 1/1/2014 United Kingdom ... 2014 1 159.0
1 52390 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.2
2 52391 1/1/2014 Canada ... 2014 1 119.2
3 52392 1/1/2014 United States ... 2014 1 159.0
4 52393 1/1/2014 United Kingdom ... 2014 1 159.0
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
14962 65773 12/31/2016 United Kingdom ... 2016 12 139.0
14963 65774 12/31/2016 United States ... 2016 12 149.0
14964 65775 12/31/2016 Canada ... 2016 12 125.3
14965 65776 12/31/2016 Germany ... 2016 12 199.0
14966 65777 12/31/2016 Germany ... 2016 12 125.1
[14967 rows x 12 columns]# Dropping columns
df_pd.drop(columns =['SIZE_EUROPE', 'SIZE_UK'], axis=1)\
.pipe(lambda x: x.info())<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 14967 entries, 0 to 14966
Data columns (total 12 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 INVOICENO 14967 non-null object
1 DATE 14967 non-null object
2 COUNTRY 14967 non-null object
3 PRODUCTID 14967 non-null object
4 SHOP 14967 non-null object
5 GENDER 14967 non-null object
6 SIZE_US 14967 non-null float64
7 UNITPRICE 14967 non-null int64
8 DISCOUNT 14967 non-null float64
9 YEAR 14967 non-null int64
10 MONTH 14967 non-null object
11 SALEPRICE 14967 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(3), int64(2), object(7)
memory usage: 1.4+ MB# Rearranging columns
# Sorting Alphabetically
df_pd.reindex(sorted(df_pd.columns), axis =1) COUNTRY DATE DISCOUNT ... SIZE_US UNITPRICE YEAR
0 United Kingdom 1/1/2014 0.0 ... 11.0 159 2014
1 United States 1/1/2014 0.2 ... 11.5 199 2014
2 Canada 1/1/2014 0.2 ... 9.5 149 2014
3 United States 1/1/2014 0.0 ... 9.5 159 2014
4 United Kingdom 1/1/2014 0.0 ... 9.0 159 2014
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
14962 United Kingdom 12/31/2016 0.0 ... 9.5 139 2016
14963 United States 12/31/2016 0.0 ... 12.0 149 2016
14964 Canada 12/31/2016 0.3 ... 10.5 179 2016
14965 Germany 12/31/2016 0.0 ... 9.5 199 2016
14966 Germany 12/31/2016 0.1 ... 6.5 139 2016
[14967 rows x 14 columns]# Rearranging columns
# Sorting As You Want (ASY)
col_first = ['YEAR','MONTH']
col_rest = df_pd.columns.difference(col_first, sort=False).to_list()
df_pd2 = df_pd [col_first +col_rest]
df_pd2.info()<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 14967 entries, 0 to 14966
Data columns (total 14 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 YEAR 14967 non-null int64
1 MONTH 14967 non-null object
2 INVOICENO 14967 non-null object
3 DATE 14967 non-null object
4 COUNTRY 14967 non-null object
5 PRODUCTID 14967 non-null object
6 SHOP 14967 non-null object
7 GENDER 14967 non-null object
8 SIZE_US 14967 non-null float64
9 SIZE_EUROPE 14967 non-null object
10 SIZE_UK 14967 non-null float64
11 UNITPRICE 14967 non-null int64
12 DISCOUNT 14967 non-null float64
13 SALEPRICE 14967 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(4), int64(2), object(8)
memory usage: 1.6+ MB3.9.4 4th Verb - rename () Function
df |>
rename(INVOICE = INVOICENO,
PRODUCT = PRODUCTID) |>
glimpse()Rows: 14,967
Columns: 14
$ INVOICE <dbl> 52389, 52390, 52391, 52392, 52393, 52394, 52395, 52396, 52…
$ DATE <date> 2014-01-01, 2014-01-01, 2014-01-01, 2014-01-01, 2014-01-0…
$ COUNTRY <chr> "United Kingdom", "United States", "Canada", "United State…
$ PRODUCT <chr> "2152", "2230", "2160", "2234", "2222", "2173", "2200", "2…
$ SHOP <chr> "UK2", "US15", "CAN7", "US6", "UK4", "US15", "GER2", "CAN5…
$ GENDER <chr> "Male", "Male", "Male", "Female", "Female", "Male", "Femal…
$ SIZE_US <dbl> 11.0, 11.5, 9.5, 9.5, 9.0, 10.5, 9.0, 10.0, 10.5, 9.0, 10.…
$ SIZE_EUROPE <chr> "44", "44-45", "42-43", "40", "39-40", "43-44", "39-40", "…
$ SIZE_UK <dbl> 10.5, 11.0, 9.0, 7.5, 7.0, 10.0, 7.0, 9.5, 10.0, 7.0, 9.5,…
$ UNITPRICE <dbl> 159, 199, 149, 159, 159, 159, 179, 169, 139, 149, 129, 169…
$ DISCOUNT <dbl> 0.0, 0.2, 0.2, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.1…
$ YEAR <dbl> 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014…
$ MONTH <dbl> 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1…
$ SALEPRICE <dbl> 159.0, 159.2, 119.2, 159.0, 159.0, 159.0, 179.0, 169.0, 13…(df_pd.rename(columns = {"PRODUCTID": "PRODUCT", "INVOICENO": "INVOICE"})
.pipe(lambda x: x.info())
)<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 14967 entries, 0 to 14966
Data columns (total 14 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 INVOICE 14967 non-null object
1 DATE 14967 non-null object
2 COUNTRY 14967 non-null object
3 PRODUCT 14967 non-null object
4 SHOP 14967 non-null object
5 GENDER 14967 non-null object
6 SIZE_US 14967 non-null float64
7 SIZE_EUROPE 14967 non-null object
8 SIZE_UK 14967 non-null float64
9 UNITPRICE 14967 non-null int64
10 DISCOUNT 14967 non-null float64
11 YEAR 14967 non-null int64
12 MONTH 14967 non-null object
13 SALEPRICE 14967 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(4), int64(2), object(8)
memory usage: 1.6+ MB3.9.5 5th Verb - mutate () Function
df |>
mutate(NECOLUMN = 5,
SALESPRICE2 = UNITPRICE*(1-DISCOUNT)) |>
glimpse()Rows: 14,967
Columns: 16
$ INVOICENO <dbl> 52389, 52390, 52391, 52392, 52393, 52394, 52395, 52396, 52…
$ DATE <date> 2014-01-01, 2014-01-01, 2014-01-01, 2014-01-01, 2014-01-0…
$ COUNTRY <chr> "United Kingdom", "United States", "Canada", "United State…
$ PRODUCTID <chr> "2152", "2230", "2160", "2234", "2222", "2173", "2200", "2…
$ SHOP <chr> "UK2", "US15", "CAN7", "US6", "UK4", "US15", "GER2", "CAN5…
$ GENDER <chr> "Male", "Male", "Male", "Female", "Female", "Male", "Femal…
$ SIZE_US <dbl> 11.0, 11.5, 9.5, 9.5, 9.0, 10.5, 9.0, 10.0, 10.5, 9.0, 10.…
$ SIZE_EUROPE <chr> "44", "44-45", "42-43", "40", "39-40", "43-44", "39-40", "…
$ SIZE_UK <dbl> 10.5, 11.0, 9.0, 7.5, 7.0, 10.0, 7.0, 9.5, 10.0, 7.0, 9.5,…
$ UNITPRICE <dbl> 159, 199, 149, 159, 159, 159, 179, 169, 139, 149, 129, 169…
$ DISCOUNT <dbl> 0.0, 0.2, 0.2, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.1…
$ YEAR <dbl> 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014, 2014…
$ MONTH <dbl> 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1…
$ SALEPRICE <dbl> 159.0, 159.2, 119.2, 159.0, 159.0, 159.0, 179.0, 169.0, 13…
$ NECOLUMN <dbl> 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5…
$ SALESPRICE2 <dbl> 159.0, 159.2, 119.2, 159.0, 159.0, 159.0, 179.0, 169.0, 13…df_pd['NEWCOLUMN'] = 5
df_pd.info() <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 14967 entries, 0 to 14966
Data columns (total 15 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 INVOICENO 14967 non-null object
1 DATE 14967 non-null object
2 COUNTRY 14967 non-null object
3 PRODUCTID 14967 non-null object
4 SHOP 14967 non-null object
5 GENDER 14967 non-null object
6 SIZE_US 14967 non-null float64
7 SIZE_EUROPE 14967 non-null object
8 SIZE_UK 14967 non-null float64
9 UNITPRICE 14967 non-null int64
10 DISCOUNT 14967 non-null float64
11 YEAR 14967 non-null int64
12 MONTH 14967 non-null object
13 SALEPRICE 14967 non-null float64
14 NEWCOLUMN 14967 non-null int64
dtypes: float64(4), int64(3), object(8)
memory usage: 1.7+ MBdf_pd.drop(columns = ['NEWCOLUMN'], axis = 1, inplace = True)
df_pd.info() <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 14967 entries, 0 to 14966
Data columns (total 14 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 INVOICENO 14967 non-null object
1 DATE 14967 non-null object
2 COUNTRY 14967 non-null object
3 PRODUCTID 14967 non-null object
4 SHOP 14967 non-null object
5 GENDER 14967 non-null object
6 SIZE_US 14967 non-null float64
7 SIZE_EUROPE 14967 non-null object
8 SIZE_UK 14967 non-null float64
9 UNITPRICE 14967 non-null int64
10 DISCOUNT 14967 non-null float64
11 YEAR 14967 non-null int64
12 MONTH 14967 non-null object
13 SALEPRICE 14967 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(4), int64(2), object(8)
memory usage: 1.6+ MBdf_pd['SALEPRICE2']=df_pd['UNITPRICE']*(1-df_pd['DISCOUNT'])
df_pd.info()<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 14967 entries, 0 to 14966
Data columns (total 15 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 INVOICENO 14967 non-null object
1 DATE 14967 non-null object
2 COUNTRY 14967 non-null object
3 PRODUCTID 14967 non-null object
4 SHOP 14967 non-null object
5 GENDER 14967 non-null object
6 SIZE_US 14967 non-null float64
7 SIZE_EUROPE 14967 non-null object
8 SIZE_UK 14967 non-null float64
9 UNITPRICE 14967 non-null int64
10 DISCOUNT 14967 non-null float64
11 YEAR 14967 non-null int64
12 MONTH 14967 non-null object
13 SALEPRICE 14967 non-null float64
14 SALEPRICE2 14967 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(5), int64(2), object(8)
memory usage: 1.7+ MB# Using the assign() function
(df_pd[['PRODUCTID', 'UNITPRICE', 'DISCOUNT']]\
.assign(SALEPRICE3 =lambda x: x.UNITPRICE*(1-x.DISCOUNT)) \
.head(5)
) PRODUCTID UNITPRICE DISCOUNT SALEPRICE3
0 2152 159 0.0 159.0
1 2230 199 0.2 159.2
2 2160 149 0.2 119.2
3 2234 159 0.0 159.0
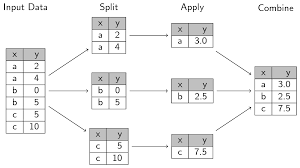
4 2222 159 0.0 159.03.9.6 6th Verbs - group_by () and summarize () Functions
Figure 3.1 presents Split Apply Combine principle in group_by () and summarize () functions.
df |>
group_by(COUNTRY) |>
summarize (AVGPRICE = mean(UNITPRICE, na.rm = TRUE))# A tibble: 4 × 2
COUNTRY AVGPRICE
<chr> <dbl>
1 Canada 165.
2 Germany 164.
3 United Kingdom 166.
4 United States 163.df |>
group_by(COUNTRY) |>
summarize (AVGPRICE = mean(UNITPRICE, na.rm = TRUE),
AVGSALEPRICE = mean (SALEPRICE, na.rm = TRUE))# A tibble: 4 × 3
COUNTRY AVGPRICE AVGSALEPRICE
<chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Canada 165. 144.
2 Germany 164. 144.
3 United Kingdom 166. 146.
4 United States 163. 144.# Summary Statistics
df %>%
select(UNITPRICE, SALEPRICE) %>%
summarize(across(where(is.numeric),
.fns = list(N = ~length(.),
Mean = mean,
Std = sd,
Median = median,
P25 = ~quantile(.,0.25),
P75 = ~quantile(., 0.75)
)
)) %>%
pivot_longer(everything(), names_sep='_', names_to=c('variable', '.value')) # A tibble: 2 × 7
variable N Mean Std Median P25 P75
<chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 UNITPRICE 14967 164. 22.9 159 149 179
2 SALEPRICE 14967 144. 35.2 149 125. 169df_pd.groupby(['COUNTRY'])['UNITPRICE'].mean()COUNTRY
Canada 164.691057
Germany 164.163934
United Kingdom 165.614853
United States 163.490316
Name: UNITPRICE, dtype: float64df_pd.groupby(['COUNTRY'])[['UNITPRICE', 'SALEPRICE']].mean() UNITPRICE SALEPRICE
COUNTRY
Canada 164.691057 144.228963
Germany 164.163934 143.574658
United Kingdom 165.614853 145.505872
United States 163.490316 143.727421df_pd.groupby(['COUNTRY']) [['UNITPRICE', 'SALEPRICE']] \
.agg(np.mean) UNITPRICE SALEPRICE
COUNTRY
Canada 164.691057 144.228963
Germany 164.163934 143.574658
United Kingdom 165.614853 145.505872
United States 163.490316 143.727421df_pd.groupby(['COUNTRY']) [['UNITPRICE', 'SALEPRICE']] \
.agg("mean") UNITPRICE SALEPRICE
COUNTRY
Canada 164.691057 144.228963
Germany 164.163934 143.574658
United Kingdom 165.614853 145.505872
United States 163.490316 143.727421df_pd.groupby(['COUNTRY']) [['UNITPRICE', 'SALEPRICE']] \
.agg(AVG_UNITPRICE =("UNITPRICE","mean"),
AVG_LISTPRICE =("SALEPRICE","mean")) AVG_UNITPRICE AVG_LISTPRICE
COUNTRY
Canada 164.691057 144.228963
Germany 164.163934 143.574658
United Kingdom 165.614853 145.505872
United States 163.490316 143.727421df_pd.groupby(['COUNTRY']) [['UNITPRICE', 'SALEPRICE']] \
.agg(AVG_UNITPRICE =("UNITPRICE","mean"),
AVG_LISTPRICE =("SALEPRICE","mean"),
TOTALN=("SALEPRICE","size"), # size function for n
TOTALOBS=("SALEPRICE","count") # count function for n
) AVG_UNITPRICE AVG_LISTPRICE TOTALN TOTALOBS
COUNTRY
Canada 164.691057 144.228963 2952 2952
Germany 164.163934 143.574658 4392 4392
United Kingdom 165.614853 145.505872 1737 1737
United States 163.490316 143.727421 5886 5886# Defining a Function
def percentile(n):
def percentile_(x):
return x.quantile(n)
percentile_.__name__ ='percentile_{:02.0f}'.format(n*100)
return percentile_
# Some summary statistics
df_pd[['UNITPRICE', 'SALEPRICE']] \
.agg(['count', 'mean', 'std', 'median', percentile(0.25), percentile (0.75)]) \
.transpose() \
.reset_index() \
.rename(columns = {"index": "variables", "percentile_25": "P25", "percentile_75": "P75", 'count': "N"}) \
.round(3) variables N mean std median P25 P75
0 UNITPRICE 14967.0 164.171 22.941 159.0 149.0 179.0
1 SALEPRICE 14967.0 143.988 35.181 149.0 125.1 169.0# Summary Statistics
agg_dict = {
"N": "count",
'Mean':"mean",
"Std. Dev" : "std",
'P25': lambda x: x.quantile(0.25),
'Median': 'median',
'p75': lambda x: x.quantile(0.75)
}
df_pd[['UNITPRICE', 'SALEPRICE']].agg(agg_dict)3.10 Reshaping Data
Before we discuss about reshaping of the data, we need to discuss about tidy format of the data. Data can come in many shapes, but not all shapes are useful for data analysis. In most cases, tidy format of the data is most useful for analysis. Therefore, if the data is untidy, we need to make it tidy first. There are three interrelated rules which make a dataset tidy (Wickham, Çetinkaya-Rundel, and Grolemund 2023). These rules are given below. Figure 3.2 visually represents tidy principle.
Each variable must have its own column
Each observation must have its own row
Each value must have its own cell
For analysis, many times we need to change the format of our dataset and we call it reshaping. Data come primarily in two shapes -wide and long. Sometimes wide format is called “record” format and long format is called “stacked” format. In wide format data, there is one row for each subject (units of observation). Data is long when there are multiple rows for each subject (units of observations).
This reshaping can be two types - a) long to wide and 2) wide to long. Long-to-wide means reshaping a long data, which has many rows, into wide format, which has many variables. In wide-to-long format, we do otherwise. For analytical purpose, reshaping data is useful; so, we need to know how to do the reshaping.
Whether a given dataset (e.g., Table 3.2) is in wide or long format depends on our research questions (on what variables we are interested in and how we conceive of our data). If we are interested in variable Temp and Month variable is the unit of obsevation, then the dataset in Table 3.2 is in long format because Month is repeated in mutiple rows.
airquality = airquality
examp = airquality |>
slice(1:10)3.10.1 Long-to-Wide Format
To make a long dataset to wide, we can use pivot_wider() function from tidyr package in R and pivot() function from pandas in python.
tidyr::us_rent_income# A tibble: 104 × 5
GEOID NAME variable estimate moe
<chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 01 Alabama income 24476 136
2 01 Alabama rent 747 3
3 02 Alaska income 32940 508
4 02 Alaska rent 1200 13
5 04 Arizona income 27517 148
6 04 Arizona rent 972 4
7 05 Arkansas income 23789 165
8 05 Arkansas rent 709 5
9 06 California income 29454 109
10 06 California rent 1358 3
# ℹ 94 more rowstidyr::us_rent_income |>
pivot_wider(
names_from = variable,
values_from = c(estimate, moe)
)# A tibble: 52 × 6
GEOID NAME estimate_income estimate_rent moe_income moe_rent
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 01 Alabama 24476 747 136 3
2 02 Alaska 32940 1200 508 13
3 04 Arizona 27517 972 148 4
4 05 Arkansas 23789 709 165 5
5 06 California 29454 1358 109 3
6 08 Colorado 32401 1125 109 5
7 09 Connecticut 35326 1123 195 5
8 10 Delaware 31560 1076 247 10
9 11 District of Columbia 43198 1424 681 17
10 12 Florida 25952 1077 70 3
# ℹ 42 more rows# install palmerpenguins package
# pip install palmerpenguins
import palmerpenguins
penguins = palmerpenguins.load_penguins()penguins[["island", "bill_length_mm"]] \
.pivot(columns = "island", values = "bill_length_mm") \
.fillna(0)island Biscoe Dream Torgersen
0 0.0 0.0 39.1
1 0.0 0.0 39.5
2 0.0 0.0 40.3
3 0.0 0.0 0.0
4 0.0 0.0 36.7
.. ... ... ...
339 0.0 55.8 0.0
340 0.0 43.5 0.0
341 0.0 49.6 0.0
342 0.0 50.8 0.0
343 0.0 50.2 0.0
[344 rows x 3 columns]3.10.2 Wide-to-Long Format
To make a wide dataset to long, we can use pivot_longer() function from tidyr package in R and melt() function from pandas in python.
relig_income# A tibble: 18 × 11
religion `<$10k` `$10-20k` `$20-30k` `$30-40k` `$40-50k` `$50-75k` `$75-100k`
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Agnostic 27 34 60 81 76 137 122
2 Atheist 12 27 37 52 35 70 73
3 Buddhist 27 21 30 34 33 58 62
4 Catholic 418 617 732 670 638 1116 949
5 Don’t k… 15 14 15 11 10 35 21
6 Evangel… 575 869 1064 982 881 1486 949
7 Hindu 1 9 7 9 11 34 47
8 Histori… 228 244 236 238 197 223 131
9 Jehovah… 20 27 24 24 21 30 15
10 Jewish 19 19 25 25 30 95 69
11 Mainlin… 289 495 619 655 651 1107 939
12 Mormon 29 40 48 51 56 112 85
13 Muslim 6 7 9 10 9 23 16
14 Orthodox 13 17 23 32 32 47 38
15 Other C… 9 7 11 13 13 14 18
16 Other F… 20 33 40 46 49 63 46
17 Other W… 5 2 3 4 2 7 3
18 Unaffil… 217 299 374 365 341 528 407
# ℹ 3 more variables: `$100-150k` <dbl>, `>150k` <dbl>,
# `Don't know/refused` <dbl>relig_income |>
pivot_longer(
cols = !c(religion),
names_to = "income",
values_to = "count"
)# A tibble: 180 × 3
religion income count
<chr> <chr> <dbl>
1 Agnostic <$10k 27
2 Agnostic $10-20k 34
3 Agnostic $20-30k 60
4 Agnostic $30-40k 81
5 Agnostic $40-50k 76
6 Agnostic $50-75k 137
7 Agnostic $75-100k 122
8 Agnostic $100-150k 109
9 Agnostic >150k 84
10 Agnostic Don't know/refused 96
# ℹ 170 more rowspenguins.melt(value_vars=["bill_length_mm", "bill_depth_mm","flipper_length_mm", "body_mass_g"],
id_vars = ['species', 'island', 'sex', 'year']
) species island sex year variable value
0 Adelie Torgersen male 2007 bill_length_mm 39.1
1 Adelie Torgersen female 2007 bill_length_mm 39.5
2 Adelie Torgersen female 2007 bill_length_mm 40.3
3 Adelie Torgersen NaN 2007 bill_length_mm NaN
4 Adelie Torgersen female 2007 bill_length_mm 36.7
... ... ... ... ... ... ...
1371 Chinstrap Dream male 2009 body_mass_g 4000.0
1372 Chinstrap Dream female 2009 body_mass_g 3400.0
1373 Chinstrap Dream male 2009 body_mass_g 3775.0
1374 Chinstrap Dream male 2009 body_mass_g 4100.0
1375 Chinstrap Dream female 2009 body_mass_g 3775.0
[1376 rows x 6 columns]3.11 Merging Datasets
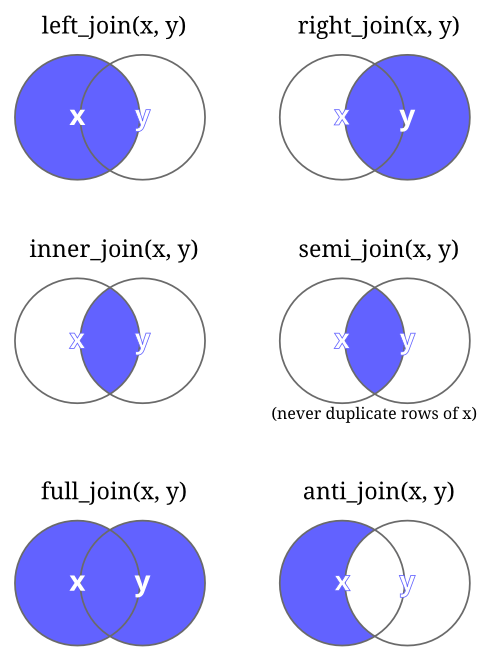
Many times, for analysis purposes, we need to join two datasets. This process is also called merging3. There are different types of joining. So, it is important to learn about those joining techniques. In Figure 3.3 shows the joining technique and functions using dplyr in R. Below all of these joining functions are explained.
left_join(): The merged dataset contains all observations fromthe first (or left) dataset and only matched observations from the second (or right) datasetright_join(): The merged dataset contains only matched observations from the first (or left) dataset and all observations from the second (or right) datasetinner_join(): The merged dataset contains only matched observations from both datasetssemi_join(): The merged dataset contains matched observations from the first (or left) dataset. Please note thatsemi_join()differs frominner_join()in thatinner_join()will return one row of first dataset (x) for each matching row of second dataset (y), whereassemi_join()will never duplicate rows of x.full_join(): The merged dataset contains all observations from both datasetsanti_join(): The merged dataset contains only not matched observations from the first (or left) dataset and contains only the variable from the left dataset
Table 3.3 compares the dplyr joining functions with equivalent joining functions from pandas.
| dplyr | pandas | Description |
|---|---|---|
| left_join() | pd.merge(df1, df2, on='key', how='left') | Join matching rows from df2 to df1, keeping all rows from df1. |
| right_join() | pd.merge(df1, df2, on='key', how='right') | Join matching rows from df1 to df2, keeping all rows from df2. |
| inner_join() | pd.merge(df1, df2, on='key', how='inner') | Join matching rows from both dataframes (default behavior of merge()). |
| full_join() | pd.merge(df1, df2, on='key', how='outer') | Join all rows from both dataframes, filling missing values with NaN. |
| semi_join() | No direct equivalent, but can be achieved using filtering | Keep rows in df1 where a match exists in df2. |
| anti_join() | No direct equivalent, but can be achieved using filtering | Keep rows in df1 where no match exists in df2. |
data1 = read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/msharifbd/DATA/refs/heads/main/DATA.csv")
glimpse(data1)Rows: 6,910
Columns: 14
$ companyname <chr> "AMERICAN AIRLINES GROUP INC", "AMERICAN AIRLINES GROU…
$ stateincorp <chr> "DE", "DE", "DE", "DE", "DE", "DE", "DE", "DE", "DE", …
$ ticker <chr> "AAL", "AAL", "AAL", "AAL", "AAL", "AAL", "AAL", "AAL"…
$ year <dbl> 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016, …
$ sic <dbl> 4512, 4512, 4512, 4512, 4512, 4512, 4512, 4512, 4512, …
$ totalassets <dbl> 25175.000, 25438.000, 25088.000, 23848.000, 23510.000,…
$ costofgoodssold <dbl> 20232.000, 16935.000, 18138.000, 20420.000, 20529.000,…
$ netincome <dbl> -2071.000, -1468.000, -471.000, -1979.000, -1876.000, …
$ sale <dbl> 23766.000, 19917.000, 22170.000, 24022.000, 24855.000,…
$ advertising <dbl> 153.000, 153.000, 165.000, 186.000, 153.000, 166.000, …
$ sellingadmin <dbl> 3024.000, 2720.000, 2729.000, 2907.000, 2892.000, 4672…
$ mktvalue <dbl> 2976.3858, 2571.1835, 2597.5755, 117.3438, 266.5571, 6…
$ commonequity <dbl> -2935.000, -3489.000, -3945.000, -7111.000, -7987.000,…
$ totalliability <dbl> 28110.000, 28927.000, 29033.000, 30959.000, 31497.000,…data2 = read_csv("https://github.com/msharifbd/DATA/raw/refs/heads/main/DATA2.csv")
glimpse(data2)Rows: 43,147
Columns: 13
$ ticker <chr> "MLP", "MLP", "MLP", "RCPIQ", "RCPIQ", "RCPI…
$ cik_code <dbl> 63330, 63330, 63330, 776008, 776008, 776008,…
$ auditor <chr> "Accuity LLP", "Accuity LLP", "Accuity LLP",…
$ INTERNALCONTROL_EFFECTIVE <chr> "Yes", "Yes", "Yes", "Yes", "Yes", "Yes", "N…
$ year_ended_date <date> 2017-12-31, 2018-12-31, 2019-12-31, 2004-12…
$ financials_date <date> 2017-12-31, 2018-12-31, 2019-12-31, 2004-12…
$ fiscal_year <dbl> 2017, 2018, 2019, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 20…
$ signature_date <date> 2018-02-23, 2019-03-01, 2020-02-28, 2005-04…
$ NUMBEROFCONTROLWEAKNESS <dbl> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,…
$ audit_fees <dbl> 206000, 209000, 213000, 224209, 382454, 4155…
$ non_audit_fees <dbl> 29000, 30000, 30000, 188081, 92869, 61351, 3…
$ year <dbl> 2017, 2018, 2019, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 20…
$ big4 <dbl> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,…# left_join
left_join(data1, data2, by = c("ticker", "year"))# A tibble: 6,969 × 25
companyname stateincorp ticker year sic totalassets costofgoodssold
<chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 AMERICAN AIRLINES… DE AAL 2008 4512 25175 20232
2 AMERICAN AIRLINES… DE AAL 2009 4512 25438 16935
3 AMERICAN AIRLINES… DE AAL 2010 4512 25088 18138
4 AMERICAN AIRLINES… DE AAL 2011 4512 23848 20420
5 AMERICAN AIRLINES… DE AAL 2012 4512 23510 20529
6 AMERICAN AIRLINES… DE AAL 2013 4512 42278 19084
7 AMERICAN AIRLINES… DE AAL 2014 4512 43771 29511
8 AMERICAN AIRLINES… DE AAL 2015 4512 48415 25416
9 AMERICAN AIRLINES… DE AAL 2016 4512 51274 25695
10 AMERICAN AIRLINES… DE AAL 2017 4512 51396 28262
# ℹ 6,959 more rows
# ℹ 18 more variables: netincome <dbl>, sale <dbl>, advertising <dbl>,
# sellingadmin <dbl>, mktvalue <dbl>, commonequity <dbl>,
# totalliability <dbl>, cik_code <dbl>, auditor <chr>,
# INTERNALCONTROL_EFFECTIVE <chr>, year_ended_date <date>,
# financials_date <date>, fiscal_year <dbl>, signature_date <date>,
# NUMBEROFCONTROLWEAKNESS <dbl>, audit_fees <dbl>, non_audit_fees <dbl>, …# left_join
left_join(data1 |> distinct(ticker, year, .keep_all = TRUE),
data2 |> distinct(ticker, year, .keep_all = TRUE),
by = c("ticker", "year")
)# A tibble: 6,910 × 25
companyname stateincorp ticker year sic totalassets costofgoodssold
<chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 AMERICAN AIRLINES… DE AAL 2008 4512 25175 20232
2 AMERICAN AIRLINES… DE AAL 2009 4512 25438 16935
3 AMERICAN AIRLINES… DE AAL 2010 4512 25088 18138
4 AMERICAN AIRLINES… DE AAL 2011 4512 23848 20420
5 AMERICAN AIRLINES… DE AAL 2012 4512 23510 20529
6 AMERICAN AIRLINES… DE AAL 2013 4512 42278 19084
7 AMERICAN AIRLINES… DE AAL 2014 4512 43771 29511
8 AMERICAN AIRLINES… DE AAL 2015 4512 48415 25416
9 AMERICAN AIRLINES… DE AAL 2016 4512 51274 25695
10 AMERICAN AIRLINES… DE AAL 2017 4512 51396 28262
# ℹ 6,900 more rows
# ℹ 18 more variables: netincome <dbl>, sale <dbl>, advertising <dbl>,
# sellingadmin <dbl>, mktvalue <dbl>, commonequity <dbl>,
# totalliability <dbl>, cik_code <dbl>, auditor <chr>,
# INTERNALCONTROL_EFFECTIVE <chr>, year_ended_date <date>,
# financials_date <date>, fiscal_year <dbl>, signature_date <date>,
# NUMBEROFCONTROLWEAKNESS <dbl>, audit_fees <dbl>, non_audit_fees <dbl>, …dataset1 = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/msharifbd/DATA/refs/heads/main/DATA.csv")
dataset2 = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/msharifbd/DATA/raw/refs/heads/main/DATA2.csv",encoding="latin-1")pd.merge(dataset1, dataset2, on=['ticker', 'year'], how='left') companyname stateincorp ... non_audit_fees big4
0 AMERICAN AIRLINES GROUP INC DE ... 990000.0 1.0
1 AMERICAN AIRLINES GROUP INC DE ... 1446000.0 1.0
2 AMERICAN AIRLINES GROUP INC DE ... 1455000.0 1.0
3 AMERICAN AIRLINES GROUP INC DE ... 2645000.0 1.0
4 AMERICAN AIRLINES GROUP INC DE ... 1989000.0 1.0
... ... ... ... ... ...
6964 INFOSONICS CORP -OLD MD ... NaN NaN
6965 INFOSONICS CORP -OLD MD ... NaN NaN
6966 INFOSONICS CORP -OLD MD ... NaN NaN
6967 INFOSONICS CORP -OLD MD ... NaN NaN
6968 INFOSONICS CORP -OLD MD ... NaN NaN
[6969 rows x 25 columns]dataset1_drop = dataset1.drop_duplicates(subset=['ticker', 'year'], ignore_index = True)
dataset2_drop = dataset2.drop_duplicates(subset=['ticker', 'year'], ignore_index = True)
pd.merge(dataset1_drop, dataset2_drop, on=['ticker', 'year'], how='left') companyname stateincorp ... non_audit_fees big4
0 AMERICAN AIRLINES GROUP INC DE ... 990000.0 1.0
1 AMERICAN AIRLINES GROUP INC DE ... 1446000.0 1.0
2 AMERICAN AIRLINES GROUP INC DE ... 1455000.0 1.0
3 AMERICAN AIRLINES GROUP INC DE ... 2645000.0 1.0
4 AMERICAN AIRLINES GROUP INC DE ... 1989000.0 1.0
... ... ... ... ... ...
6905 INFOSONICS CORP -OLD MD ... NaN NaN
6906 INFOSONICS CORP -OLD MD ... NaN NaN
6907 INFOSONICS CORP -OLD MD ... NaN NaN
6908 INFOSONICS CORP -OLD MD ... NaN NaN
6909 INFOSONICS CORP -OLD MD ... NaN NaN
[6910 rows x 25 columns]df1 = pd.DataFrame({'id': [1, 2, 3], 'value': ['A', 'B', 'C']})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'id': [2, 3, 4], 'other_value': ['X', 'Y', 'Z']})
# Left join
left_join = pd.merge(df1, df2, on='id', how='left')
# Inner join
inner_join = pd.merge(df1, df2, on='id')
# Semi join
semi_join = df1[df1['id'].isin(df2['id'])]
# Anti join
anti_join = df1[~df1['id'].isin(df2['id'])]